GenAI Systems Improving at Completing Longer Tasks
A new study by METR (Model Evaluation & Threat Research) shows GenAI systems are getting exponentially better at completing longer tasks, doubling their capabilities every 7 months.
Key Findings From the Report:
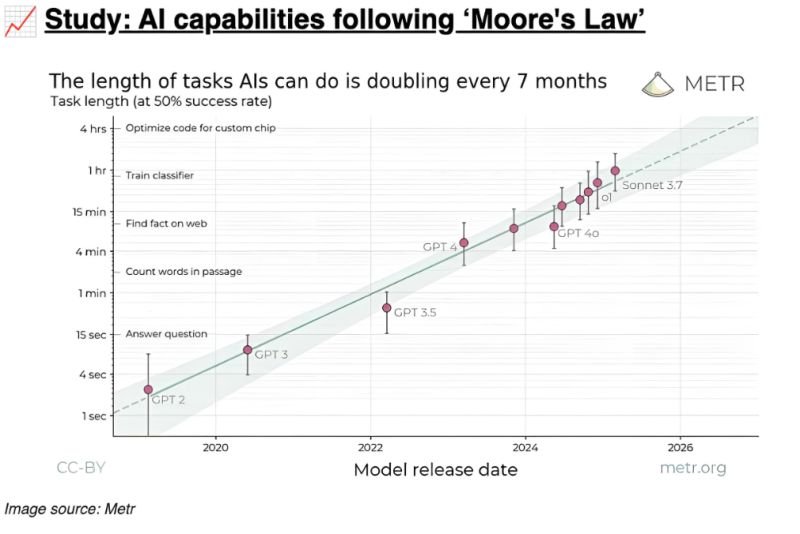
Researchers introduced the "50%-task-completion time horizon" as a new metric - the time humans typically take to complete tasks that AI models can complete with a 50% success rate.
Current frontier AI models (like Claude 3.7 Sonnet) have a time horizon of approximately 50 minutes.
AI time horizon has doubled approximately every seven months since 2019, with an acceleration in 2024.
Improvements appear driven by greater reliability, ability to adapt to mistakes, and enhanced logical reasoning and tool use capabilities.
Testing across 170 tasks of varying difficulty from software engineering, cybersecurity, and ML research showed consistent exponential improvement.
There's a clear pattern: models have almost 100% success on tasks taking humans <4 minutes, but <10% success on tasks taking humans >4 hours.
Analysis suggests that if trends continue, within 5 years, AI systems could be capable of automating many software tasks that currently take humans days or weeks to complete
This research provides a helpful quantitative framework for measuring AI capabilities against human performance. It also provides even more evidence of why AI literacy and training are imperative now as the technology's capacity grows exponentially.